Client
Cimolai technology SPA
Category
CAE ANALYSIS AND CALCULATIONS, FEM STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS, MECHANICAL DESIGN, EXCEPTIONAL LOAD HANDLING, AEROSPACE/SPACE LOGISTICS
Tags
FATIGUE ANALYSIS, WELDED STRUCTURES, STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION
Millimeter alignment, safety and handling time
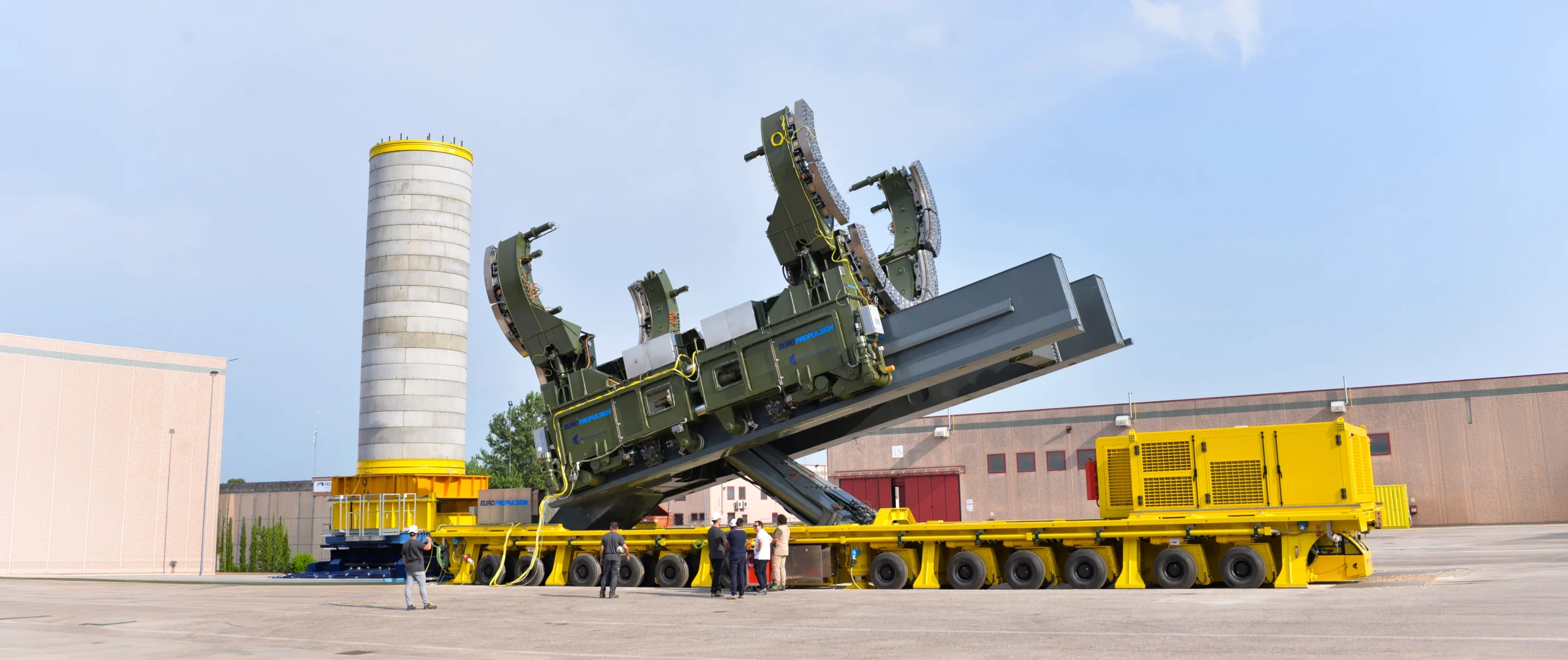
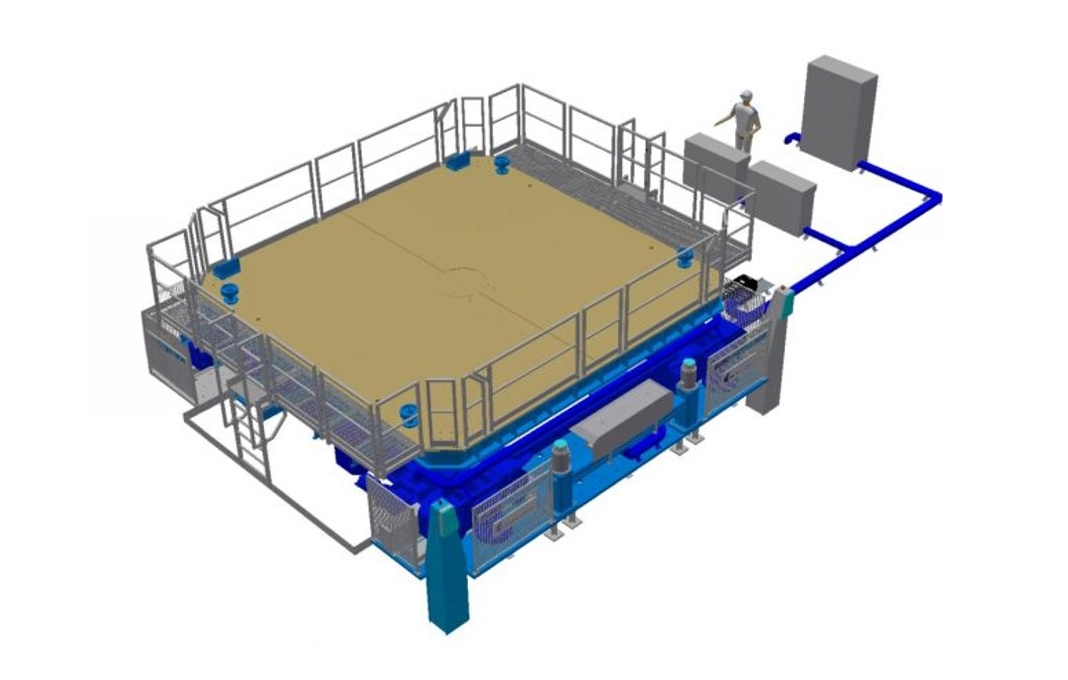
Design and FEM analysis of a multidirectional conveyor for aerospace components.
Those who work inaerospace know that handling is the most critical moment: all it takes is one positioning error and, as a result, you risk damaging a component worth a fortune. For this project, we designed a modular system capable of handling complex rotations and tilts directly on the shop floor. In addition, the structural (FEM) calculations were key to “targeting” the design: the goal was not to build a tank, but an optimized structure that would withstand fatigue loads while maintaining the required safety margins.
Customer & request
For Cimolai Technology we were in charge of one of the most delicate phases of the Ariane 6 program: the handling of the PC120C module. The requirement, in fact, was not trivial: we needed a system capable not only of translating but also of rotating and tilting the component for proper alignment. Moreover, in addition to the mechanical design, we handled all the structural checks because, when moving segments of a launcher, regulatory compliance is not just bureaucracy: it is ensuring that nothing gives way while maneuvering tons of space technology.
Accuracy of
alignment
Material reduction
via FEM optimization
Reduced average time of
handling
Safety Compliance
aerospace
Multidirectional conveyor design problem on heavy-load platform: complex maneuvering with risk on stability and accuracy
The need was to realize a system capable of:
- move in two directions (longitudinal movement and lateral adjustments),
- Manage platform rotation and controlled load tipping,
- Ensuring millimeter placements during alignment steps,
- Comply with stringent safety requirements and industry regulations,
- Optimize time and cost of implementation.
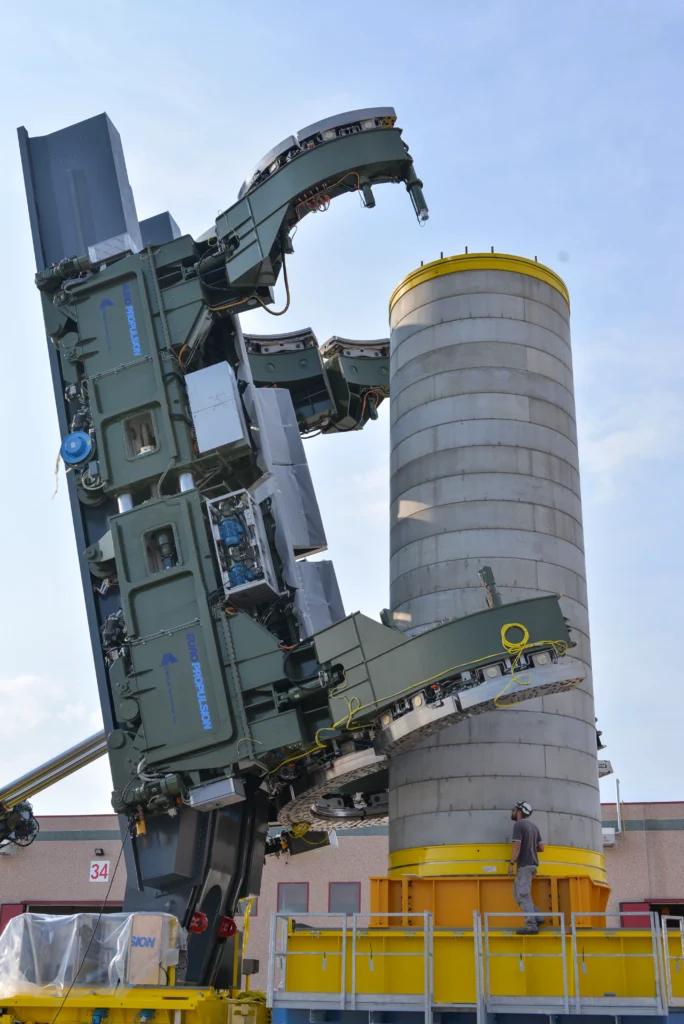

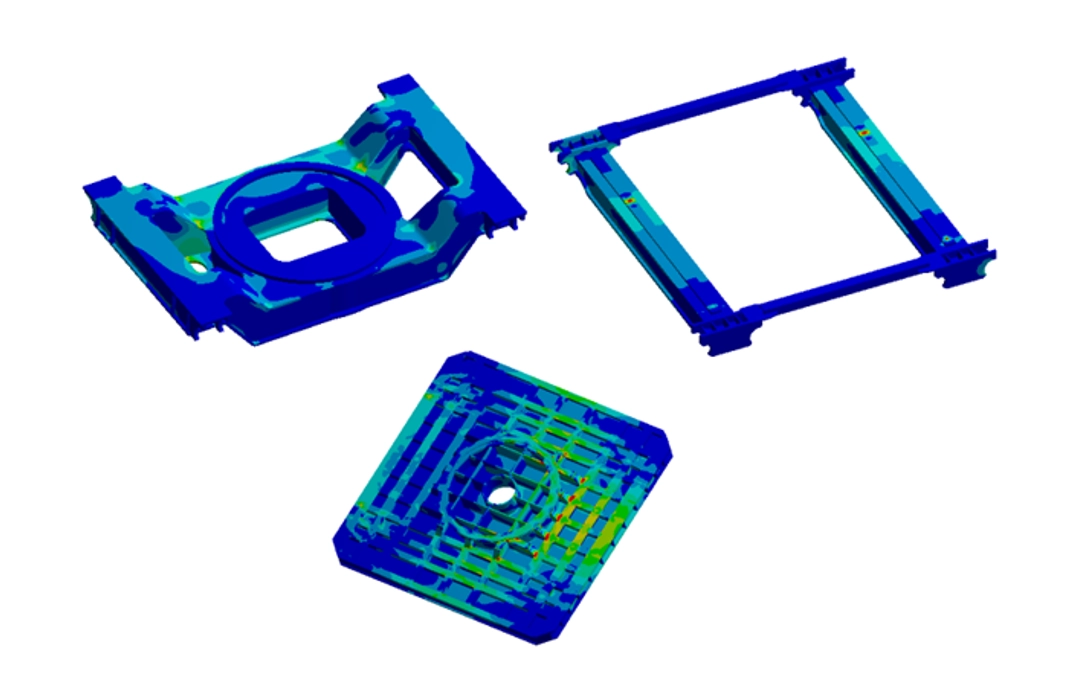
Objectives of structural FEM analysis on modular conveyor: accuracy, safety, timing, and material use
L'FEM analysis was not just to confirm that the structure did not collapse: on the contrary, the real goal was to remove material where it was not needed. Indeed, we often tend to oversize to be safe; however, a conveyor that is too heavy becomes slow and difficult to handle, especially when you have to make fine alignments. Consequently, the simulation allowed us to see where the structure flexed too much during tipping-the critical moment for stability-and then stiffen only those points, lightening the rest. Basically, it's a balancing act: we wanted robust safety margins, but without wasting steel.
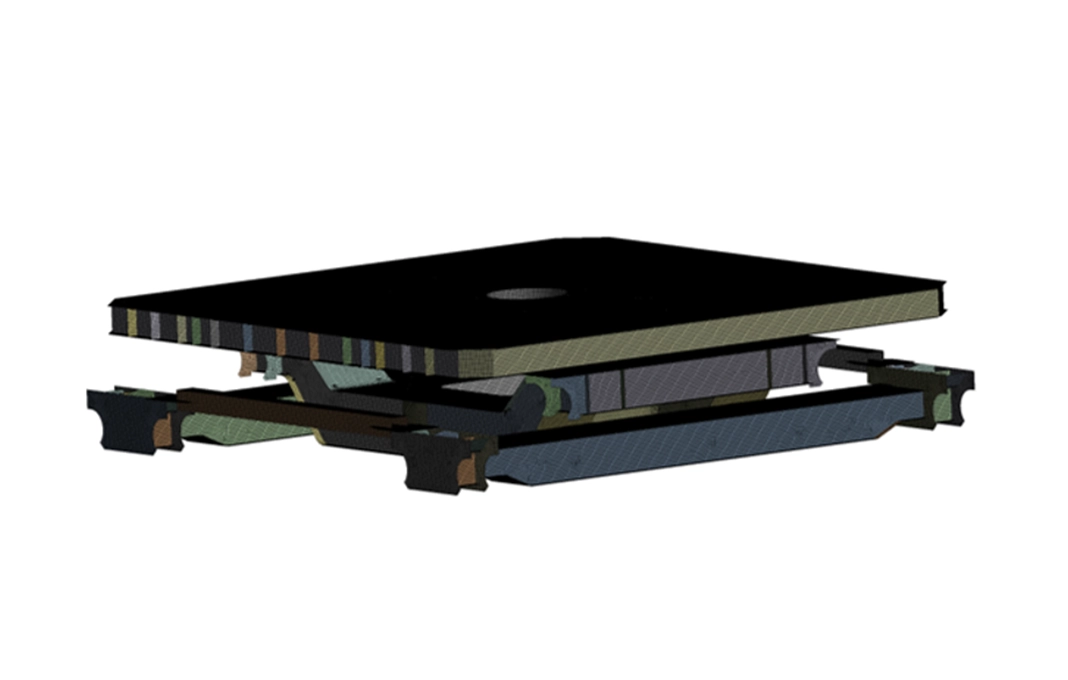
3-level technical architecture (moving base, slewing ring, horizontal alignment)
The conveyor was designed as a modular structure with three independent levels:
Mobile base structure: movement along the main axis of loading (longitudinal movement).
Slewing ring: rotation of the entire platform with angular control for positioning and tilting.
Horizontal alignment system: fine lateral adjustments for millimeter placements.
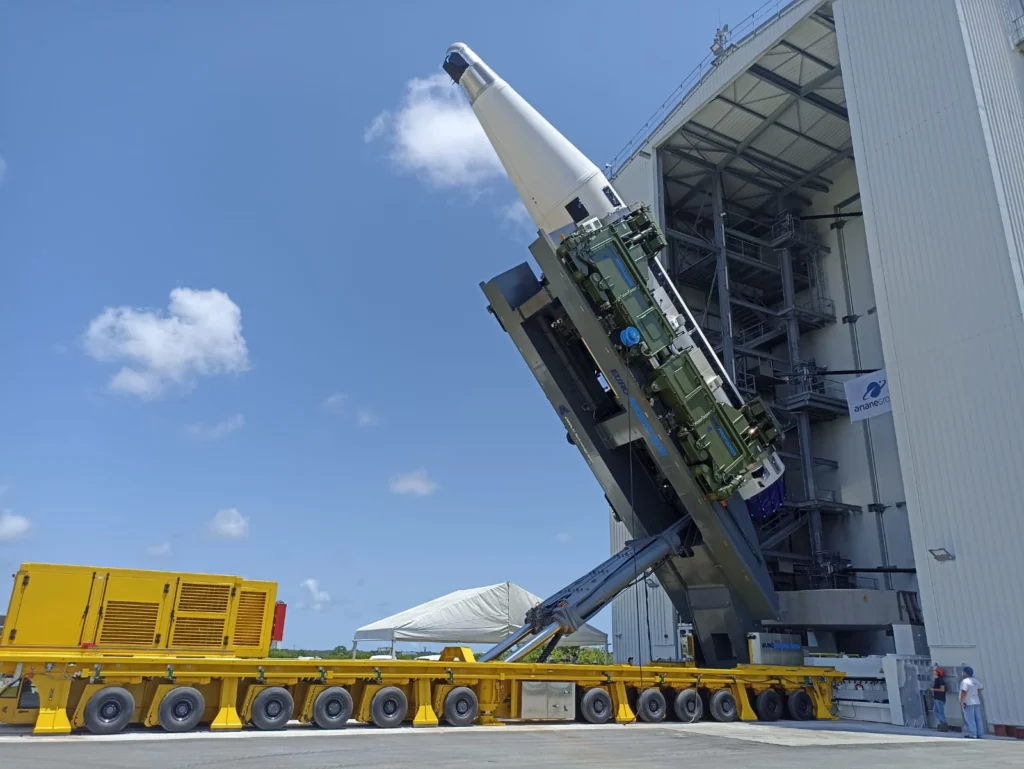

Design results and FEM analysis on conveyor: alignment ±1 mm, -20% material, -35% time
The results reported by the project include a set of technical and operational indicators. The platform achieves ±1 mm alignment and rotation accuracy, which was achieved by the dedicated level of alignment and functional separation. In addition, FEM-guided structural optimization resulted in a reported reduction in material use of -20%. From an operational point of view, consequently, a 35% reduction in average handling time compared to previous solutions is indicated. 100% compliance with industry safety regulations is also stated.